Developing Smart Energy Systems for Future Cities

July 25,2019,Philippines—As technology advances, we witness faster connectivity, increased convenience, better personalization, and many more improvements in our world. However, the rate at which new technologies are being introduced has been problematic, at least in recent years.
To keep up with the rapid technological advancements as well as not to lose their market to the competition, the global manufacturing industry has to constantly upgrade their systems and products. In order to do this fast and without sacrificing quality and cost, the global manufacturing industry, along with the rest of the world, has become heavily dependent on fossil fuels which is not only harmful for the environment, but is also slowly diminishing.
It also does not help that 68% of the world’s population in 2050 are expected to live in urban areas, according to the report Urbanization by Our World in Data from 2018, due to various reasons such as employment and better lifestyle. This prediction is presenting growing problems of poverty and environmental degradation, especially for urbanized areas.
There is no better time to invest in renewable energy market and to start developing different smart energy systems to replace fossil fuels than today. Fortunately, several forward-thinking cities are already in the process of developing smart energy systems for the future.
Renewable energy source
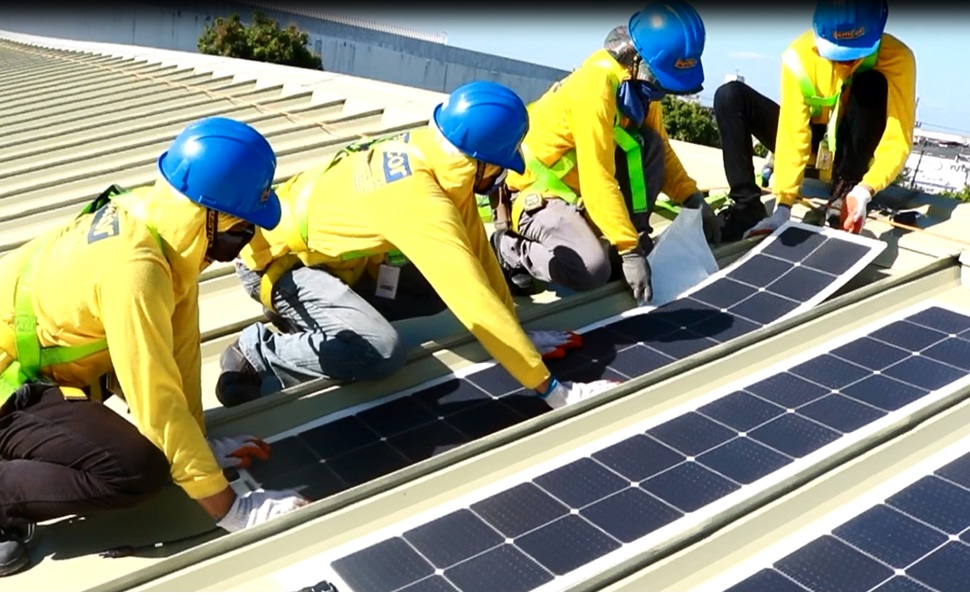
Many industries, especially the transport sector, still remain heavily reliant on fossil fuels. However, REN21 in their Renewables 2019 Global Status Report shows hope by reporting that the renewable energy technologies saw a relatively stable market in 2018 with electricity generated from wind and solar photovoltaics (PV) becoming more economical than power from fossil fuel-fired plants in many places by the end of the year.
That said, wind and solar PV seem to be the best candidates in terms of new major energy sources, although there are several other renewable energy sources city officials may develop as well, including space-based solar power, tidal power, hydrogen power, and more.
Energy storage
Before the wind, solar PV, and other renewable energy sources become mainstream technologies in the future, the renewable energy market must figure out how to create the appropriate energy storage to save electricity for later use as soon as possible. This is extremely important for the renewable energy market as most, if not all, renewable energy sources are intermittent and not constantly present.
Additionally, the electricity grid requires equal power supply and demand at any given time, which means that output fluctuations from renewable energy sources like wind and solar PV will increase the complexity of operating it. Thus, energy storage is necessary in order to balance power and create a more reliable grid system.
The current dominant energy storage technology, lithium-ion battery, can handle renewable energy power, but it is typically for short-term use only which may just be a source of a problem later on. There are redox flow or vanadium flow batteries, however, which can last for 20 years and are capable of providing hundreds of megawatt-hour at grid-scale, emerging on the market, but they are still in their early stages and are still very expensive to be commercially used.
Smart microgrids
For a more convenient and smoother operation of smart energy systems, the renewable energy market and the rest of the global manufacturing industry must produce and utilize smart microgrids which are a combination of smart grids and microgrids.
A smart grid is basically the electric grid that distributes electricity from the source to different locations except that it allows for two-way communication between the utility and the customers. Together with smart meters, smart grids allow energy from renewable energy sources to be optimized.
Meanwhile, microgrid is a localized power grid that can operate on its own or in conjunction with the main power source. With its ability to work independently of the grid, microgrids can protect communities from outages during natural disasters as well as reach areas that were previously unreached by conventional power suppliers.
Combining the two concepts, smart microgrids will transform consumers into “prosumers” who can use, distribute, and profit from the energy they generate amongst themselves.
Although it still has a long way to go, the future of smart energy systems is looking great so far. However, the shift to smart energy systems might come faster if the numerous EMS company in the Philippines and other countries, together with local governments, join forces to abandon the use of fossil fuels and rally for a stronger renewable energy market.
Other Blog