How 3D Printing Helps Aerospace Take Off

In early May 2024, the lead partner of an Innovate UK-funded project, Rivelin Robotics announced that it was set to deliver a “complete digital post-processing solution” for at least three industries, including aerospace using Additive Manufacturing (AM, or 3D printing).
What’s groundbreaking about this development is related to addressing prior challenges when it comes to post-processing metal parts, which are known to be expensive, labor-intensive, dirty, and often dangerous. Other considerations in conventional post-processing of metal parts take into account lead times, quality control, repeatability, and high costs.
The project called CAMPFIRE (Certified Additive Manufactured Parts Finished with Intelligent Robotics Engine) hopes to circumvent previous challenges with their metal post-processing solution for GKN Aerospace.
(Also Read: How 3D Printing Breaks Manufacturing Rules in the Best Way)
Metal post-processing is just one step where additive manufacturing shines in the aerospace industry. Other steps where AM is involved in the processes cover design, preparation, and testing. Post-processing is the step that happens when the parts or components are taken off from the build tray. Everything 3D printed requires post-processing, which refines the component into its finished form. 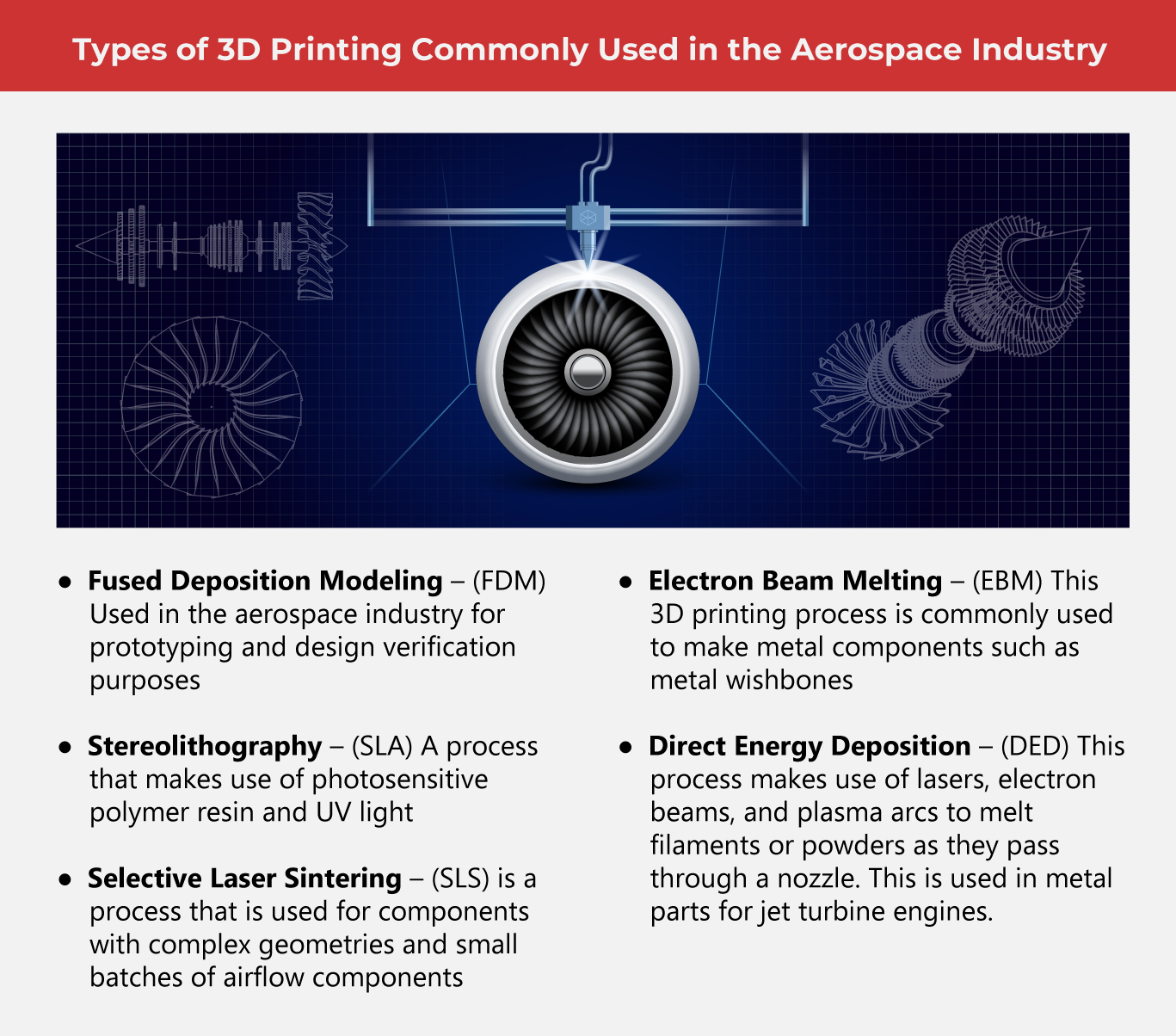
How the Aerospace Industry Stands to Benefit from Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing transforms three main areas in the aerospace industry: design, manufacturing, and maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO).
Design – The aerospace industry benefits from the freedom additive manufacturing offers in designing complex geometries and lattice structures. Engineers can create intricate components that are lighter in weight and have better performance.
Weight Reduction – Lighter aircraft = fewer carbon emissions, which is why lighter-weight components are critical when in the aerospace industry. Additive manufacturing allows engineers to explore alternative materials that are strong and lightweight.
Prototypes and Production – Additive printing has freed manufacturing constraints when it comes to creating prototypes. By reducing lead times and lowering material costs, engineers have more legroom when it comes to manufacturing prototypes for design verification, testing, and spotting areas of improvement.
Customization – The customization of components becomes much easier and tailor-fit for particular specifications.
Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul – Additive manufacturing has made it easier and more efficient to repair or replace components and spare parts.
Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace Action
Here are a few notable projects that demonstrate just how impactful additive manufacturing is in the aerospace industry.
Gravity Industries 3D-printed jet suits – Developing jet suits designed for search and rescue, Gravity Industries was able to turn around prototypes quickly and more efficiently through additive manufacturing. Its test pilot and lead designer, Sam Rogers was able to choose better and more affordable material to create prototypes during design tests.
A&M Tool and Design makes custom-made machines for aerospace – Here’s a quick study of faster turnaround time for the A&M Tool and Design team. Thanks to 3D printing, the team can produce prototypes round the clock for testing the very next day.
Lufthansa Technik’s MRO strategy – Lufthansa Technik is one of the aerospace industry’s giants when it comes to maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO). They have developed proprietary escape route markings called Guide U, made for installation on aircraft cabins. These special markings glow in the dark in case of emergencies when the power aboard the aircraft fails. These were created via additive manufacturing.
Elliptika’s 3D-printed electroplates – This company produces radio frequency and microwave products such as antennas. They work with various industries including defense, medicine, and aerospace. Elliptika makes use of 3D printing techniques such as stereolithography (SLA) to make their antennas.
NASA tests out 3d-printed components in space – Scientists and researchers at NASA want to find out about the performance of 3d-printed electroplated parts in space, so through Alpha Space’s International Space Station test platform MISSE-16 (Materials International Space Station Experiment), the prototypes will be sent to space and then returned to earth after some time for further testing.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog