What EV Charger Is Perfect for You

Electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids are gaining traction in the automotive market, becoming increasingly popular and sought after. As demand for EVs grows, current and prospective owners need guidance in navigating the various charging options available. Understanding these charging solutions is essential for being future-ready, and optimizing the EV ownership experience.
Getting to know the electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a type of car that runs on electricity instead of fuel. Unlike an electronic vehicle, which refers to any vehicle with electronic components, an electric vehicle uses a battery-powered electric motor for propulsion. From cars and buses to trains and motorcycles, EVs are gaining popularity for their cost-efficiency and sustainability.
EVs have several types, each with different power sources and capabilities:
-
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These fully electric vehicles run only on a rechargeable battery, with no fuel engine.
-
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
By combining an electric motor and battery with a fuel engine, these can run on electric power alone for short distances and switch to fuel when needed.
-
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs)
These EVs use both a fuel engine and an electric motor but don’t need to be plugged in; the battery is charged by the engine and regenerative braking.
-
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
This EV generates electricity using hydrogen fuel cells instead of batteries, emitting only water vapor as a byproduct.
What are the different EV charging levels?
EVs utilize three main charging levels—each designed to meet different needs and provide varying charging speeds for optimal convenience and efficiency.
Level 1 Charging
- Voltage: 120 volts
- Charging Speed: Adds about 3 to 5 miles of range per hour.
- Usage: Ideal for overnight charging at home or for short commutes. It does not require special equipment, as it uses a regular electrical outlet.
Level 2 Charging
- Voltage: 240 volts
- Charging Speed: Adds about 10 to 60 miles of range per hour, depending on the vehicle and charger specifications.
- Usage: Commonly found in homes with dedicated charging stations and at public charging locations. It is suitable for daily charging needs and faster recharging.
DC Fast Charging (Level 3 Charging)
- Voltage: 480 volts or more
- Charging Speed: Can add 60 to 100 miles of range in approximately 20 to 30 minutes.
- Usage: Primarily used at public charging stations along highways and in urban areas for quick recharges during long trips. Not all EVs are compatible with DC fast charging.
Where can you charge your EV?
Here’s a guide to finding the best places to keep your vehicle powered up.
-
Home charging
Most electric car and plug-in hybrid owners charge primarily at home—over 80% of charging sessions take place there. Home charging is the most convenient, but many drivers still supplement it with public charging, found in businesses, parking lots, or paid stations along longer routes. With new EV models boasting upgraded batteries capable of 300+ miles per charge, many drivers with shorter commutes can meet most, if not all, of their charging needs at home.
Pros
- Convenience: Charge your vehicle overnight or anytime at home, saving trips to public stations.
- Cost savings: Residential electricity rates are generally lower than public charging fees, reducing long-term charging costs.
- Time efficiency: Eliminate wait times at public charging stations and start each day with a full battery.
Cons
- Upfront installation costs: Installing a Level 2 charger at home can be costly, with equipment and installation potentially eating into your budget, depending on electrical setup and necessary upgrades.
- Slower charging on standard outlets: Using a standard 120V outlet (Level 1) is very slow and may take more than 24 hours to fully charge some EVs, which may not be suitable for drivers with longer daily commutes.
- Space requirements: A dedicated area, often in a garage or driveway, is typically needed for charging, which may be a constraint for those without private parking.
-
Public charging
Public charging allows EV drivers to recharge their cars during trips that surpass their battery's available range. These charging stations are commonly found near establishments like eateries, retail centers, parking areas, and other public locations. To charge an EV at a public station, you typically need to sign up for a subscription with the network that manages and maintains the charger.
Pros
- Extended range: Public charging stations allow drivers to recharge their vehicles during long trips, overcoming range anxiety and enabling longer journeys.
- Convenience: Many public charging stations are strategically located near amenities such as shopping centers, restaurants, and parking lots, making it easy to charge while running errands.
- Fast charging options: Some public stations offer fast charging (DC fast chargers), significantly reducing charging time compared to standard home charging.
Cons
- Limited availability: Public charging stations may not always be conveniently located, leading to potential difficulties in finding a charger, especially in rural or less populated areas
- Network compatibility: Some charging stations may require specific subscriptions or accounts, complicating access for drivers who are not members of that network.
- Overcrowding: High demand at popular charging locations can lead to long wait times, especially during peak travel periods.
-
Charging at work
Workplace charging operates similarly to home charging and can be provided by employers for their staff. Depending on individual commuting patterns, workplace charging may fulfill most of an employee's travel requirements. When available, employers typically offer Level 1 or Level 2 charging stations vehicles in company parking areas.
Pros
- Cost savings: Some employers provide free or subsidized charging, reducing the overall cost of vehicle operation for employees.
- Time efficiency: Charging while at work saves time since employees can utilize their work hours to recharge instead of making dedicated trips to charging stations.
- Environmental benefits: By promoting the use of electric vehicles and providing charging options, companies can contribute to reducing carbon emissions and supporting sustainability initiatives.
Cons
- Limited charging infrastructure: Not all workplaces have adequate charging stations, which can lead to insufficient charging options for employees.
- Potential for Overcrowding: If many employees drive EVs, available chargers may become overwhelmed, resulting in longer wait times to access charging.
- Not suitable for all commuters: Employees who work remotely or travel frequently may not benefit from workplace charging, making it less relevant for some staff members.
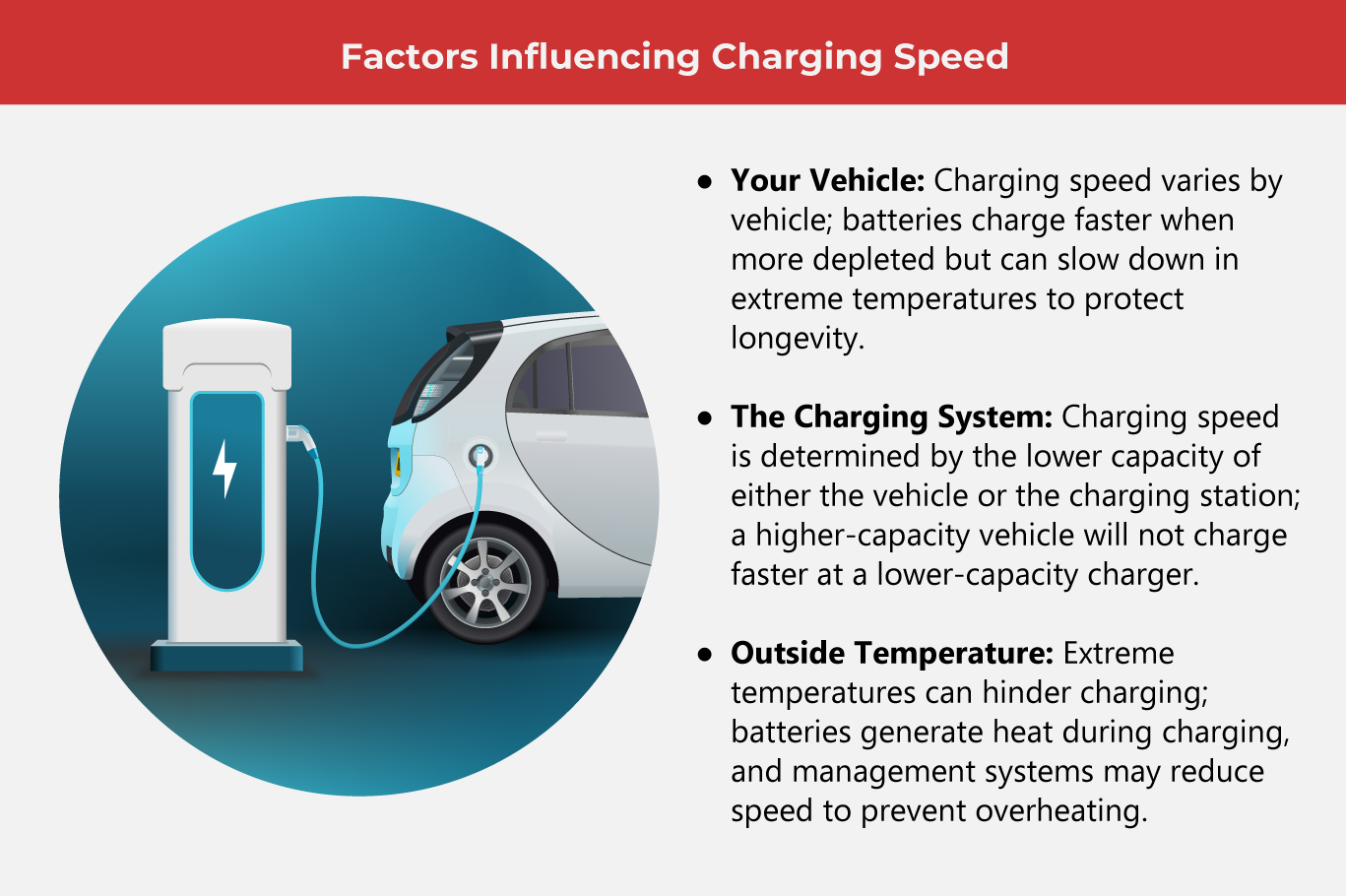 In summary, understanding EV charging is crucial for optimizing your EV ownership experience. From understanding the different charging levels to recognizing the factors that influence charging speed, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions.
In summary, understanding EV charging is crucial for optimizing your EV ownership experience. From understanding the different charging levels to recognizing the factors that influence charging speed, this knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions. As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog