SiC Semiconductors at Top Speed
SiC semiconductors are leading the way in powering up a high-voltage future. From electric vehicles to cutting-edge smartphones, these tiny tech titans are making waves in production design and development, so manufacturers are snapping them up.
When COVID-19 hit its peak, remote work and online transactions also hit an all-time high. So did the sales of mobile phones and computers, which caused a chip shortage in some market segments. This resulted in businesses ramping up their chip supply to meet the electronics demand. However, the global economy became sluggish, urging customers to spend only for essential needs. As the demand for PCs and phones declined, some chipmakers were left with excess inventory.
Still, semiconductors, including chips, remain a crucial part of modern technology. Because of their incredible ability to direct and control electrical current, semiconductors have shaped many industries and boosted energy efficiency. This has unlocked opportunities across manufacturing, healthcare, transportation and space exploration.
Enter, SiC Semiconductors
Silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors are lauded for their unique electrical capabilities, offering these benefits compared to traditional silicon semiconductors:
- High tolerance for heat
SiC boasts a wider bandgap than silicon. Bandgap is the energy gap between two parts (valence and conduction bands) of a semiconductor component. Because of this, SiC semiconductors can withstand higher temperatures compared to their full-silicon counterparts, allowing them to operate in harsh environments. This makes them dependable even in high-heat conditions like in aerospace engineering.
- High voltage capacity
The wide bandgap also translates to high voltage tolerance, which means SiC can thrive in high-energy applications, such as electric vehicles (EVs), industrial motor drives, and power distribution.
- Boosted efficiency
Efficiency translates to power optimization, reduced heat generation, and lower energy losses, essential to voltage conversion and electrical management systems.
- Fast switching rates
SiC semiconductors can be turned on and off at fast speeds, making them crucial in applications that operate at high frequencies, such as power inverters, switching power supplies, and voltage stabilizers. For instance, SiC is used in solar devices, making solar energy systems more efficient and dependable.
- Radiation resistance
Unlike silicon, which may degrade with radiation exposure, SiC can thrive in space and nuclear applications. This is because of its wide bandgap, stable lattice structure, excellent thermal conductivity, and other improved electronic properties.
How EVs' popularity is saving the semiconductor market
As chip manufacturers and vendors express concerns about sluggish sales and surplus stock, the semiconductor industry finds redemption in SiC electrical circuits utilized in EVs. While countries grapple with conflict, pandemic effects, and economic uncertainty, global efforts remain concerted toward a zero-emission future. This determined shift to green energy has governments offering incentives to EV buyers and makers, helping expand the industry. The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts global EV sales will increase by 25% by 2030.
To keep up with the demand, the world's top SiC semiconductors are ramping production, forming strategic partnerships and venturing into in-house manufacturing. During the second quarter of 2023, US-based On Semiconductor (Onsemi) stated a 26% profit boost from the previous year, with revenue from silicon carbide units quadrupling. 90% of these sales come from the auto industry, particularly e-mobility and automotive suppliers. Things are going so well that Onsemi predicts a US$2-billion revenue in the third quarter, thanks to the high vehicular demand.
SiC market milestones
Proof that SiC is leading the semiconductor market are these bits of industry news:
- SiC-based component manufacturer Wolfspeed, based in the US, announced a secured note financing deal of US$1.25 billion from an investment group, with the opportunity to secure an additional US$750 million.
- The German enterprise Bosch announced its intention to acquire US-based TSI Semiconductors through a US$1.5 billion investment. The plan is to upgrade the manufacturing facility to produce SiC parts on 200mm wafers.
- STMicroelectronics, a French-Italian multinational corporation that generates components for Tesla, is scaling up its output through in-house chip production. It expects its SiC circuits to rake in at least US$5 billion by 2030. This is also due to its expanding applications aside from EVs, including industrial and solar locomotives.
- At the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) 2023 in San Francisco in the US, Germany-based Infineon unveiled its SiC-based innovations, including a lightweight air-core motor that's half the weight of conventional motors. It is also more efficient while utilizing less copper, which equates to resource conservation. Additionally, new SiC players emerged at the convention—proof that the SiC industry is gaining attention.
- Japanese manufacturing giant Mitsubishi Electric Corporation announced that it will double its original investment of about JP¥260 billion in establishing a wafer plan to amplify its SiC power semiconductor production.
The future of SiC
SiC represents the third generation of the semiconductor industry and is poised to become a global phenomenon. For now, silicon dominates the market for power electronics in the automotive market, taking almost a 70% share. Experts forecast that though silicon and SiC will likely co-exist as preferred power components, the former will likely fade into the background after five years. Because SiC has no way to go but up, thriving in diverse applications while paving the path for new ones.
SiC is undeniably building momentum because of the increasing awareness of the significance of energy optimization, especially in consumer electronics. Third-generation semiconductors, such as SiC, are characterized by low energy consumption with high performance.
Because of SiC's benefits, manufacturers are fast-tracking the research and development phase of these semiconductors, quickly preparing them for large-scale production.
Here are some industries where SiC is making waves:
- EV sector
SiC's outstanding and dependable performance makes it a great option for vehicular power systems. Also, SiC-based systems typically require fewer components, leading to reduced size and weight—essential strategies in boosting EV performance.
SiC can also significantly lower charging time for EV batteries due to its rapid switching speed and high-power characteristics. Experts say that SiC technology can offer twice as fast as the traditional charging time.
- Data centers
The ease digitalization offers to its users is possible because of data centers. These act as the hub for data of different kinds and sizes that are crucial to business continuity and success. However, these centers consume vast amounts of electricity to keep their data machinery functioning. Cooling devices like air conditioning and ventilation systems need to be turned on at all times. SiC's thermal efficiency can lower energy consumption and costs while improving energy density.
- Energy storage systems
Considering the benefits of SiC, energy storage systems can enjoy better efficiency, ensuring they can release energy with minimal conduction losses. Faster charging rates, resilience in harsh settings, and high-temperature reliability all contribute to the long-term performance of energy storage systems.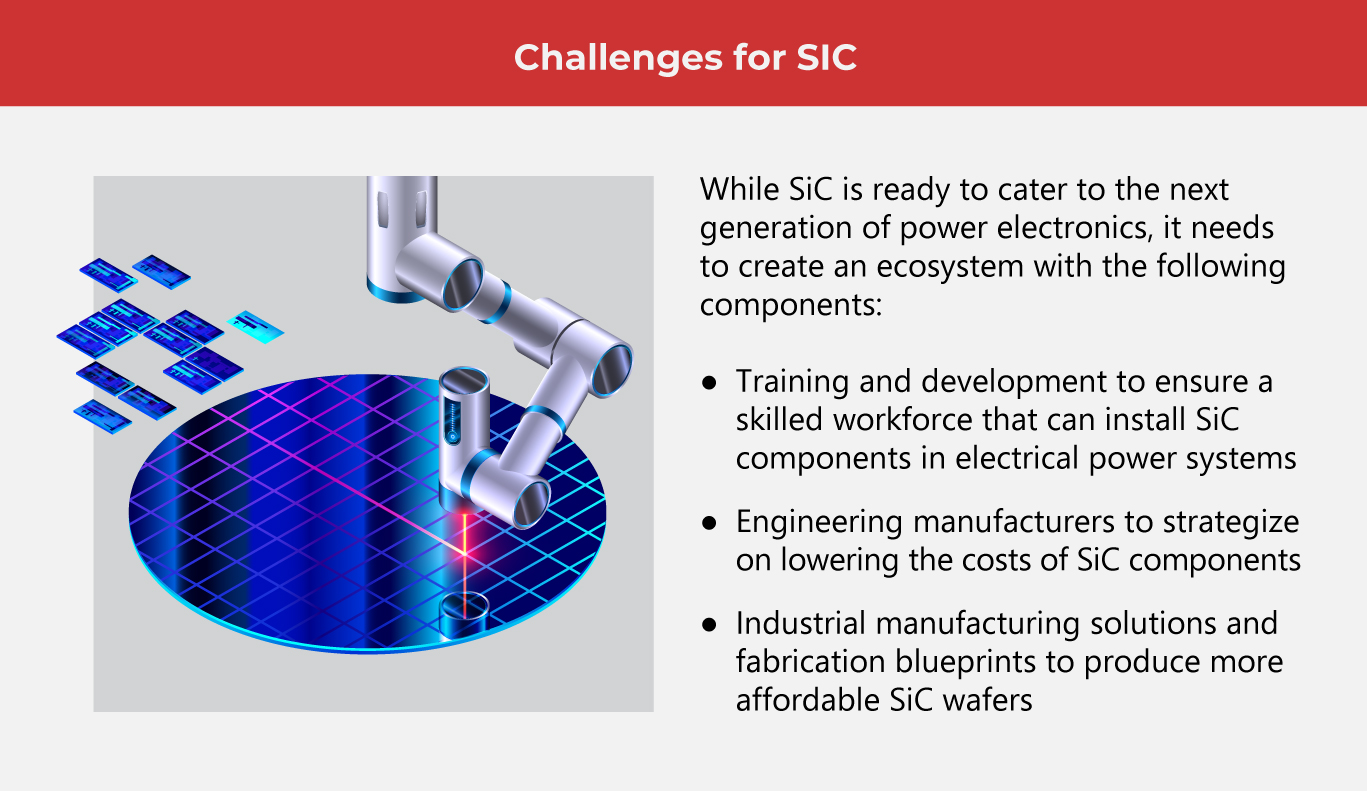

As one of the Top 20 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog