Robotics Help Aviation Reach New Heights

Both aviation and aerospace industries rely heavily on robots to meet increasing manufacturing demands. Here’s a look at some of these awesome innovations.
Market studies by ResearchandMarkets.com show that the global market size for robotics in the fields of aviation and aerospace is set to get even bigger in the years to come. With projections soaring upwards of 7B USD by 2030, this only goes to show that the demand for aircraft and the manufacture of its components are growing faster by the day.
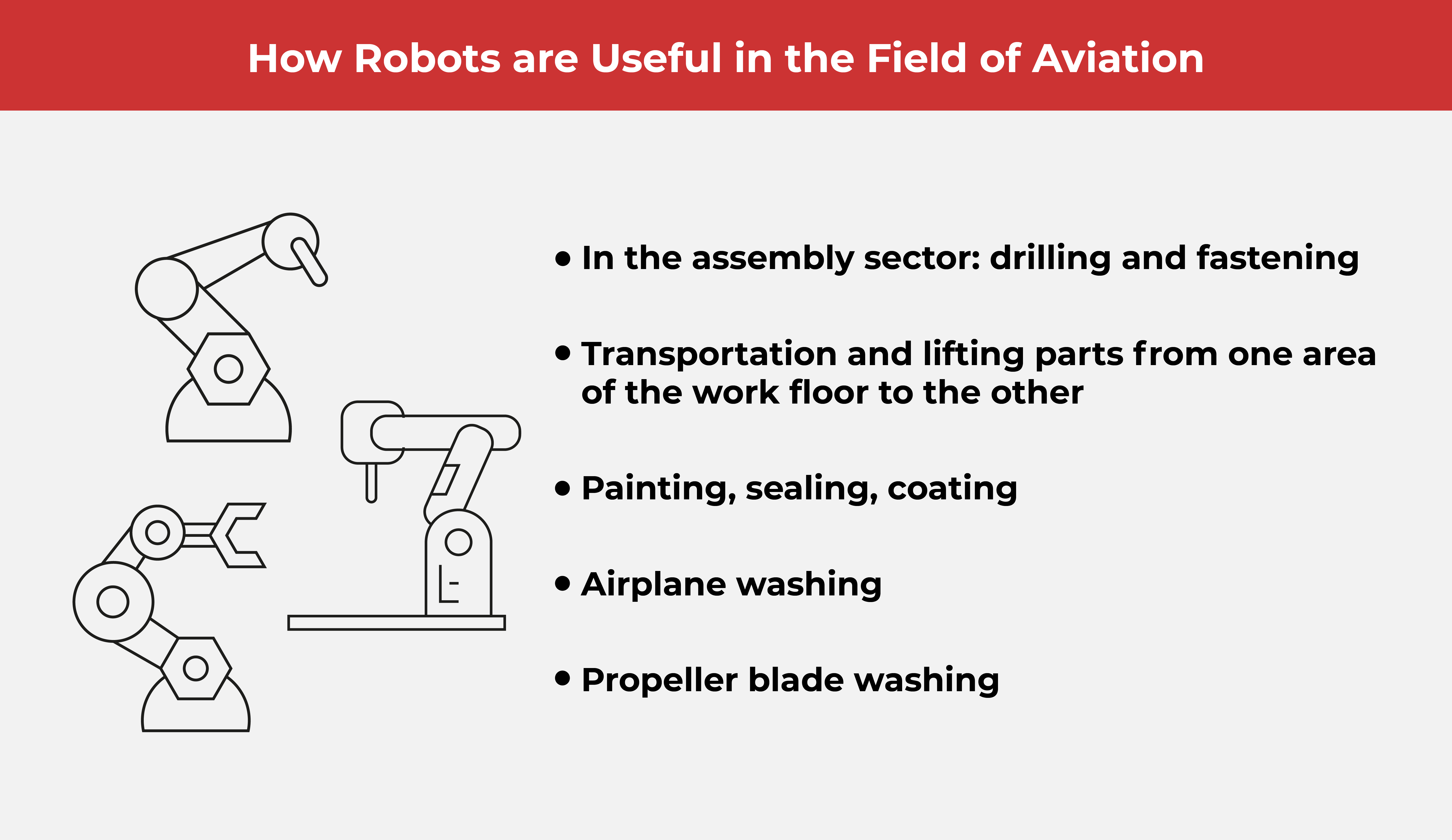
Robots have been significantly contributing to these fields for a long time already. Robots are typically found helping with attaching parts, sealing, painting, and moving heavy load through automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
When it comes to the fabrication of aircraft components, robots can also be very beneficial. Tasks such as drilling, trimming, routing, and carbon fiber layup are made much more efficient with the use of robots.
End effectors are the parts of robots that interact with their immediate surroundings, and because of the rising demand for aircraft, these have become so sophisticated as to be able to handle more delicate and complex tasks needed in the assembly and manufacture of aircraft components.
Composite-based components, such as engine rotor blades and aircraft frame structures are in-demand. Experts agree that it is in this area of the aviation and aerospace industry that will experience the most growth. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of this segment in the industry is anticipated to move faster over the eight-year forecast period.
Also in demand are applications for carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) such as forging, press unloading, foundry, handling, and processes that are part of the materials handling segment.
Robots can also be found in the surface treatment sector doing tasks such as cleaning, painting, laser treatment, and high-pressure jet washing. Often associated with tedious, repetitive, and often dangerous work, robots can be programmed to handle repetitive tasks with consistent quality throughout.
Meanwhile, over in the assembly sector, robots can be found helping with tasks such as eddy-current inspection, drilling, and welding. Because automation has become a magic word for many manufacturing industries these days, the aviation and aerospace industries have upped the level of their usage. Welding robots are becoming very popular because materials such as nickel-alloy and titanium require higher precision.
Using robots in these industrial spaces improve the structural integrity of the aircraft as well as speed up the production process. Not to mention, the use of robots also increases the safety of human workers handling these jobs at various assembly sites.
Another segment where robots contribute is in the inspection process. Sensor technology has become so advanced and intelligent these days. Sensors can detect movement, changes in the environment, and even facial features. The aviation and aerospace industries have taken advantage of these advancements in aircraft components and parts. Many companies have increased the precision of their nondestructive testing devices through the use of sensors.
Those in the industry have seen robots bolster business and allow for greater resiliency during uncertain times. After dealing with a global pandemic, these industries now have to deal with the impact of tensions from the Ukraine invasion, which is yet another element further complicating supply chains around the world.
(Also read: Unlocking the Value of Manufacturing Automation)
Supply chain robotics is used to improve supply chain resilience, and because both aviation and aerospace industries are part of the larger manufacturing industry, both should also be able to benefit from this. Supply chain robotics involves using autonomous robots to improve the processes and chains of distribution.
Robots can help ease bottlenecks, assist in critical tasks in production, and do dangerous and dull human tasks.
The challenge that aviation and aerospace industries face in terms of advancements with robotics lies in the stringent regulations set for the use of these technologies. Because of certain restrictions, aviation and aerospace manufacturers are challenged with implementing these innovations more quickly.
Experts say that for robotics to be more effective in these industries, the general rule is to start small with the deployment of robots, and with applications that will bring a strong return on investment.
The possibilities for the application of robotics in these industries signal great things not just on an industrial-level, but also on a consumer-level, too. With the automated guided vehicles already being used, it will only be a matter of time before we fully embrace unmanned automated vehicles on the streets.
The Aerospace Industries Association (AIA)seems to think this is a near reality. They project that by 2050, ordinary citizens will one day be using “flying pods” or airborne taxis to move around. Private cars, public vehicles, and yes, even ride-share cars, too. These would be flown through AI technology and will be similar and comparable to driver-less car technology.
Until that day comes, robots remain in the assembly line behind the scenes, putting together the most vital parts and components of airplanes and other forms of aircraft with the speed and efficiency of a very well-oiled intelligent machine.
As one of the Top 19 EMS companies in the world, IMI has over 40 years of experience in providing electronics manufacturing and technology solutions.
We are ready to support your business on a global scale.
Our proven technical expertise, worldwide reach, and vast experience in high-growth and emerging markets make us the ideal global manufacturing solutions partner.
Let's work together to build our future today.
Other Blog